+251 99 380 2995 | +251 97 022 2227 | [email protected]

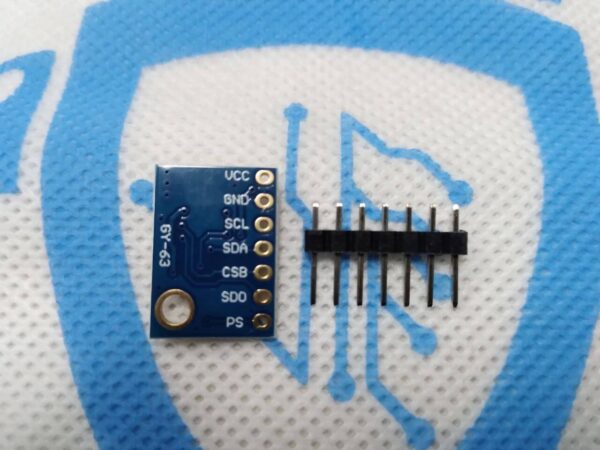
GY-63 MS5611 Pressure Temperature Sensor
Br 950.00
- GY-63 MS5611 pressure temperature sensor
- Temperature: -40 to 85°C
- Pressure: 10 to 1200 mb
- Altitude resolution: 10cm
- Fast conversion as short as 1ms
- I2C and SPI Interface
- 5V operation
- GY-63 MS5611 Pressure Temperature Sensor Module
- The MS5611 is a high precision sensor from MEAS Switzerland that can be used in many applications from portable altimeters, gaming controls and indoor navigation.
- It can take 4096 24-bit analog measurements in just 8ms and provide the average of the data points to the digital data bus. It also has built-in temperature compensation which uses the same method to filter out noise.
- The temperature measurement is primarily used to temperature compensate the pressure sensor, but it can also be used to estimate the ambient temperature as well
Measuring Temperature
- The MS5611 can measure temperature over the range of -40 to 80°C.
- Full accuracy of ±0.8°C is obtained over the entire range with a resolution of 0.01°C.
Measuring Pressure
- The MS5611 can measure pressure over the range of 10 to 1200 mbar with excellent accuracy.
- Full accuracy of ±1.5 mbar is obtained over the pressure range of 450 to 1100 mbar. Outside that pressure range the guaranteed accuracy is ±2.5 mbar
- Resolution can be as high as 0.012 mbar which gives an altitude resolution as small as 10 cm (4″).
Calculating Altitude / Elevation
- The MS5611 does not measure altitude directly, but it can be calculated using the pressure reading. Some libraries for this device include altitude calculation routines.
- Since the device does a very good job of measuring pressure, it can do a very good job of calculating relative altitude. If you have an altitude reading with the device sitting on a table and then raise it 6″, it will show a 6″ increase in altitude.
- If on the other hand you are trying to measure absolute altitude, such as the altitude of your table relative to sea level, things get more complicated. Since altitude is relative to sea level the device needs to know the current air pressure corrected to sea level so that it has a reference by which to calculate the altitude given the air pressure that it is currently reading.
Using the I2C Interface
- The I2C interface is the most used interface as it only requires two pins on the MCU.
- The PS�(Protocol Select) pin determines which bus to use. A logic HIGH selects the I2C bus. A 1K pull-up resistor on the module pulls this pin HIGH and so the I2C bus is selected by default unless this pin is grounded.
- The module supports two different I2C addresses, either 0x77 or 0x76 which allows up to 2 sensors to be used on the same bus. If the CSB pin is grounded, the address is 0x77. If it is connected to VCC the address is 0x76 (inverse logic). The CSB pin as a 2.2K pull-down resistor on the module so 0x77 is the default address if the CSB pin is not connected. Connect the CSB to Vcc to select 0x76 instead or if two sensors are used on the same I2C bus.
- The SCL and SDA pins connect to the SCL and SDA pins on the MCU.
- If more than 2 sensors are needed, then the SPI bus can be used.
Using the SPI Interface
To enable the SPI interface, connect PS�to ground.
The other connection are:
- Connect SCL pin to the SPI SCK on MCU
- Connect SDA pin to SPI SDI on MCU
- Connect SDO pin to SPI SDO on MCU
Note that logic level shifters are included on the module for these lines to make them 5V compatible.
Module Connections
The module brings out the following connections.
1 x 7 Header
- VCC = 5V nominal. Connect to 5V output of the MCU
- GND = Ground
- SCL = Clock (SCL / SCK) for I2C and SPI
- SDA = Data (SDA / SDI) for I2C and SPI
- CSB = Chip Select. Chip Select for SPI. Address select for I2C
- SDO = Data Out (SDO) for SPI
- PS = Protocol Select. Default pulled HIGH for I2C. Connect to GND for SPI






